Liberia
| Republic of Liberia | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
| Motto: "The love of liberty brought us here" | ||||||
| Anthem: All Hail, Liberia, Hail! | ||||||
 | ||||||
| Capital (and largest city) | Monrovia | |||||
| Official languages | English | |||||
| Demonym | Liberian | |||||
| Government | Republic | |||||
| - | President | Ellen Johnson-Sirleaf | ||||
| - | Vice-President | Joseph Boakai | ||||
| - | Chief Justice | Johnnie Lewis | ||||
| Formation | by African-Americans | |||||
| - | ACS colonies consolidation | 1821-1842 | ||||
| - | Independence (from the United States) | 26 July 1847 | ||||
| Area | ||||||
| - | Total | 111,369 km2 (103rd) 43,000 sq mi | ||||
| - | Water (%) | 13.514 | ||||
| Population | ||||||
| - | 2008 Liberian Census estimate | 3,489,072 (132nd) | ||||
| - | Density | 29/km2 (174th) 75/sq mi | ||||
| GDP (PPP) | 2007 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | $1.342 billion[1] | ||||
| - | Per capita | $357[1] | ||||
| GDP (nominal) | 2007 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | $735 million[1] | ||||
| - | Per capita | $195[1] | ||||
| HDI (1993) | 0.311 (low) (n/a) | |||||
| Currency | Liberian dollar1 (LRD) | |||||
| Time zone | GMT | |||||
| Drives on the | right | |||||
| Internet TLD | .lr | |||||
| Calling code | 231 | |||||
| 1 United States dollar also in common usage. | ||||||
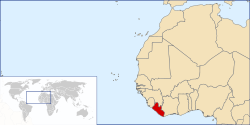
Liberia /laɪˈbɪəriə/, officially the Republic of Liberia, is a country on the west coast of Africa, bordered by Sierra Leone, Guinea, Côte d'Ivoire, and the Atlantic Ocean. As of 2008, the nation is estimated to be home to 3,489,072 people and cover 111,369 square kilometres (43,000 sq mi). Liberia has a hot equatorial climate with most rainfall arriving in summer with harsh harmattan winds in the dry season. Liberia's populated Pepper Coast is composed of mostly mangrove forests while the sparse inland is forested, later opening to a plateau of drier grasslands.
Founded as a colony in 1822 by freed slaves from the United States, the area was already inhabited by various indigenous ethnic groups who had occupied the region for centuries. In 1847, the colony of freed slaves declared independence and founded the Republic of Liberia. In 1980, the government was overturned in a military coup, and from 1989 to 2005 Liberia was in a state of flux, witnessing two civil wars, the First Liberian Civil War (1989–1996) and the Second Liberian Civil War (1999–2003) that displaced hundreds of thousands of people and devastated the country's economy.
Contents1 Etymology
|
Etymology
The name Liberia denotes "liberty" as Black Americans moved to Liberia in 1822, and founded the country in 1847 with the support of the American Colonization Society creating a new ethnic group called the Americo-Liberians.[2] However, this introduction of a new ethnic mix resulted in ethnic tensions with the sixteen other main ethnicities.[3]
History
Indigenous peoples of West Africa
Anthropological research shows the region of Liberia was inhabited at least as far back as the 12th century, perhaps earlier. Mende-speaking people expanded westward, forcing many smaller ethnic groups southward towards the Atlantic ocean. The Deys, Bassa, Kru, Gola and Kissi were some of the earliest recorded arrivals.[4] This influx was compounded during the ancient decline of the Western Sudanic Mali Empire in 1375 and later in 1591 with the Songhai Empire. Additionally, inland regions underwent desertification, and inhabitants were pressured to move to the wetter Pepper Coast. These new inhabitants brought skills such as cotton spinning, cloth weaving, iron smelting, rice and sorghum cultivation, and social and political institutions from the Mali and Songhay Empires.[5]
Shortly after the Manes conquered the region there was a migration of the Vai people into the region of Grand Cape Mount. The Vai were part of the Mali Empire who were forced to migrate when the empire collapsed in the fourteenth century. The Vai chose to migrate to the coastal region.
The ethnic Kru opposed the migration of the Vai into their region. An alliance of the Manes and Kru were able to stop the further migration of the Vai but the Vai remained in the Grand Cape Mount region (where the city of Robertsport is now located).

Littoral coast people built canoes and traded with other West Africans from Cap-Vert to the Gold Coast. Later European traders would barter various commodities and goods with local people, sometimes hoisting their canoes aboard. When the Kru began trading with Europeans, they initially traded in non-slave commodities but later became active participants in the African slave trade.
Kru laborers left their territory to work on plantations and in construction as paid laborers. Some even worked building the Suez and Panama Canals.
Another tribal group in the area was the Glebo. The Glebo were driven, as a result of the Manes invasion, to migrate to the coast of what later became Liberia.
Early European contacts
Between 1461 and late seventeenth century, Portuguese, Dutch and British traders had contacts and trading posts in Liberia. The Portuguese had named the area Costa da Pimenta, later translated as Grain Coast, because of the abundance of grains of melegueta pepper.
Settlers from the United States
In 1822, the American Colonization Society established Liberia as a place to send black people who were formerly enslaved.[6] Other African Americans, who were never enslaved, chose to emigrate to Liberia as well.[7] African-Americans gradually migrated to the colony and became known as Americo-Liberians, from whom many present day Liberians trace their ancestry. On July 26, 1847, the Americo-Liberian settlers declared the independence of the Republic of Liberia.

The settlers regarded Africa as a "Promised Land," but they did not integrate into an African society. Once in Africa, they referred to themselves as "Americans" and were recognized as such by local Africans and by British colonial authorities in neighboring Sierra Leone. The symbols of their state — its flag, motto, and seal — and the form of government that they chose reflected their American background and diaspora experience. Lincoln University (founded as Ashmun Institute for educating young blacks in Pennsylvania in 1854) played an important role in supplying Americo-Liberians leadership for the new nation. The first graduating class of Lincoln University, James R. Amos, his brother Thomas H. Amos, and Armistead Miller sailed for Liberia on the brig Mary C. Stevens in April, 1859 after graduation.
The religious practices, social customs and cultural standards of the Americo-Liberians had their roots in the antebellum American South. These ideals strongly influenced the attitudes of the settlers toward the indigenous African people. The new nation, as they perceived it, was coextensive with the settler community and with those Africans who were assimilated into it. Mutual mistrust and hostility between the "Americans" along the coast and the "Natives" of the interior was a recurrent theme in the country's history, along with (usually successful) attempts by the Americo-Liberian minority to dominate what they identified as savage native peoples. They named the land "Liberia," which in the Romance languages, and in Latin in particular, means "Land of the Free," as an homage to their freedom from slavery.
Historically, Liberia has enjoyed the support and unofficial cooperation of the United States government.[8] Liberia’s government, modeled after that of the United States, was democratic in structure, if not always in substance. After 1877 the True Whig Party monopolized political power in the country, and competition for office was usually contained within the party, whose nomination virtually ensured election. Two problems confronting successive administrations were pressure from neighboring colonial powers, Britain and France, and the threat of financial insolvency, both of which challenged the country’s sovereignty. Liberia retained its independence during the Scramble for Africa, but lost its claim to extensive territories that were annexed by Britain and France. Economic development was hindered by the decline of markets for Liberian goods in the late nineteenth century and by indebtedness on a series of loans, payments on which drained the economy.

Significant mid-twentieth century events
Two events were of particular importance in releasing Liberia from its self-imposed isolation. The first was the grant in 1926 of a large concession to the American-owned Firestone Plantation Company; that move became a first step in the (limited) modernization of the Liberian economy. The second occurred during World War II, when the United States began providing technical and economic assistance that enabled Liberia to make economic progress and introduce social change. Both the Freeport of Monrovia and Roberts International Airport were built by U.S. personnel during World War II.
In a late night raid on April 12, 1980, a successful military coup was staged by a group of noncommissioned army officers led by Master Sergeant Samuel Kanyon Doe. The soldiers were a mixture of the various ethnic groups that claimed marginalization at the hands of the minority Americo-Liberian settlers. They killed William R. Tolbert, Jr., who had been president for nine years, in his mansion. Constituting themselves the People’s Redemption Council, Doe and his associates seized control of the government and brought an end to Africa’s first republic. Significantly, Doe was the first Liberian head of state who was not a member of the Americo-Liberian elite.
In the early 1980s, the United States provided Liberia more than $500 million for pushing the Soviet Union out of the country, and for providing the US exclusive rights to use Liberia's ports and land (including allowing the CIA to use Liberian territory to spy on Libya).[citation needed]
Doe favored authoritarian policies, banning newspapers and outlawing various opposition parties. His tactic was to brand popular opposition parties as "socialist", and therefore illegal according to the Liberian constitution, while allowing less popular minor parties to remain as a token opposition. Unfortunately for Doe, popular support would then tend to realign behind one of these smaller parties, causing them to be labeled "socialist" in their turn.

In October 1985, Liberia held the first post-coup elections, ostensibly to legitimize Doe's regime. Virtually all international observers agreed that the Liberia Action Party (LAP) led by Jackson Doe (no relation) had won the election by a clear margin. After a week of counting the votes, however, Samuel Doe fired the count officials and replaced them with his own Special Election Committee (SECOM), which announced that Samuel Doe's ruling National Democratic Party of Liberia had won with 50.9% of the vote. In response, on November 12 a counter-coup was launched by Thomas Quiwonkpa, whose soldiers briefly occupied the Executive Mansion and the national radio station, with widespread support throughout the country. Three days later, Quiwonkpa's coup was overthrown. Following this failed coup, government repression intensified, as Doe's troops killed more than 2000 civilians and imprisoned more than 100 opposing politicians, including Jackson Doe, Ellen Johnson-Sirleaf and BBC journalist Isaac Bantu.
1989 and 2003 civil wars
In late 1989, a civil war began. The harsh dictatorial atmosphere that gripped the country was due in large part to Sergeant Samuel Doe's rule. An Americo-Liberian named Charles Taylor with the backing of neighboring countries such as Burkina Faso and Cote d'Ivoire entered Nimba County with around 100 men.[9] These fighters gained high levels of support with the local population who were disillusioned with their present government. A large section of the country came under the invaders' control as a result. By this time a new player had also emerged. Yormie Prince Johnson (former ally of Taylor) had formed his own army and had gained tremendous support from the Gio and Mano ethnic groups.
In August 1990, the Economic Community Monitoring Group under the Economic Community of West African States organized its own military task force to intervene in the crisis. The troops were largely from Nigeria, Guinea and Ghana. On his way out after a meeting, Doe, who was traveling only with his personal staff, was ambushed and captured by members of the Gio Tribe who were loyal to Prince Yormie Johnson. The soldiers took him to the headquarters of Johnson in neighboring Caldwell, tortured and killed him.
By this time Taylor was a prominent warlord and leader of the National Patriotic Front of Liberia. After some prompting from Taylor that the anglophone Nigerians and Ghanaians were opposed to him, Senegalese troops were brought in with some financial support from the United States.[10] Their service was however short-lived, after a major confrontation with Taylor forces in Vahun, Lofa County on 28 May 1992, when six were killed when a crowd of NPFL supporters surrounded their vehicle and demanded they surrender their jeep and weapons.[11]
By September 1990 Doe's forces controlled only a small area just outside the capital of Monrovia. After his death, and as a condition for the end of the conflict, interim president Amos Sawyer resigned in 1994, handing power to the Council of State. Taylor was elected as President in 1997, after leading a bloody insurgency backed by Libyan President Muammar al-Gaddafi. Taylor's brutal regime targeted several leading opposition and political activists. In 1998, the government sought to assassinate child rights activist Kimmie Weeks for a report he had published on its involvement in the training of child soldiers, which forced him into exile. Taylor's autocratic and dysfunctional government led to a new rebellion in 1999. More than 200,000 people are estimated to have been killed in the civil wars.
The conflict intensified in mid-2003, and the fighting moved into Monrovia. A hastily assembled force of 1000 Nigerian troops, the ECOWAS Mission In Liberia (ECOMIL), was airlifted into Liberia on August 15, 2003 to prevent the rebels from overrunning the capital city and committing revenge-inspired war crimes. Meanwhile the U.S. Joint Task Force Liberia commanded from USS Iwo Jima (LHD-7) was offshore, though only 100 of the 2,000 U.S. Marines landed to liaise with the ECOMIL force.
As the power of the government shrank and with increasing international and American pressure for him to resign, President Taylor accepted an asylum offer from Nigeria, but vowed: "God willing, I will be back." Some of the ECOMIL troops were subsequently withdrawn and at least two battalions incorporated into the 15,000 strong United Nations Mission in Liberia (UNMIL) peacekeeping force.
Transitional government and elections
After the exile of Taylor, Gyude Bryant was appointed Chairman of the transitional government in late 2003. Because of failures of the Transitional Government in curbing corruption, Liberia signed onto GEMAP, a novel anti-corruption program. The primary task of the transitional government was to prepare for fair and peaceful democratic elections. With UNMIL troops safeguarding the peace, Liberia successfully conducted presidential elections in the fall of 2005. Twenty three candidates stood for the October 11, 2005 general election, with the early favorite George Weah, internationally famous footballer, UNICEF Goodwill Ambassador and member of the Kru ethnic group expected to dominate the popular vote. No candidate took the required majority in the general election, so that a run-off between the top two vote getters, Weah and Ellen Johnson-Sirleaf, was necessary. The November 8, 2005 presidential runoff election was won decisively by Ellen Johnson-Sirleaf, a Harvard-trained economist. Both the general election and runoff were marked by peace and order, with thousands of Liberians waiting patiently in the Liberian heat to cast their ballots.
Ellen Johnson-Sirleaf presidency
Daughter of the first indigenous Liberian to be elected to the national legislature, Jahmale Carney Johnson, Ellen Johnson-Sirleaf was born in rural Liberia. She was the first elected female head of state in Africa. Johnson-Sirleaf was jailed twice during the Doe administration before escaping and going into exile.
On March 29, 2006, Charles Taylor was extradited from Nigeria to Sierra Leone, where he had been indicted by the Special Court (a war crimes tribunal). Taylor's trial by that court is being held in the Hague, for security. He is charged with crimes against humanity, violations of the Geneva Conventions and "other serious violations of international humanitarian law".[12]
President Johnson-Sirleaf has established a Truth and Reconciliation Commission to address crimes committed during the later stages of Liberia's long civil war.[13]
Human rights situation
Amnesty International summarizes in its Annual Report 2006: "Sporadic outbreaks of violence continued to threaten prospects of peace. Former rebel fighters who should have been disarmed and demobilized protested violently when they did not receive benefits. Slow progress in reforming the police, judiciary and the criminal justice system resulted in systematic violations of due process and vigilante violence against criminal suspects. Laws establishing an Independent National Commission on Human Rights and a Truth and Reconciliation Commission were adopted. Over 200,000 internally displaced people and refugees returned to their homes, although disputes over land and property appropriated during the war raised ethnic tensions. UN sanctions on the trade in diamonds and timber were renewed. Those responsible for human rights abuses during the armed conflict continued to enjoy impunity. The UN Security Council gave peacekeeping forces in Liberia powers to arrest former President Taylor and transfer him to the Special Court for Sierra Leone if he should return from Nigeria, where he continued to receive asylum. Liberia made a commitment to abolish capital punishment. A new law on rape, which initially proposed imposition of the death penalty for gang rape, was amended to provide a maximum penalty of life imprisonment."[14] Former 22nd president Charles Taylor was later captured trying to escape across the border of Cameroon and has been sent to the International Criminal Court in The Hague for trial.
Politics and Government
Liberia has a dual system of statutory law based on Anglo-American common law for the modern sector and customary unwritten law for the native sector for exclusively rural tribes.[15] Liberia's modern sector has three equal branches of government in the constitution, though in practice the executive branch headed by the President of Liberia is the strongest of the three. Following the dissolution of the Republican Party in 1876, the True Whig Party dominated the Liberian government until the 1980 coup. Currently, no party has majority control of the legislature. The longest serving president in Liberian history was William Tubman, serving from 1944 until his death in 1971. The shortest term was held by James Skivring Smith, who controlled the government for two months. However, the political process from Liberia's founding in 1847, despite widespread corruption, was very stable until the end of the First Republic in 1980.
Geography


Liberia is situated in West Africa, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean to the country's southwest. The landscape is characterized by mostly flat to rolling coastal plains that contain mangroves and swamps, which rise to a rolling plateau and low mountains in the northeast.[6] Tropical rainforests cover the hills, while elephant grass and semi-deciduous forests make up the dominant vegetation in the northern sections.[6] The equatorial climate is hot year-round with heavy rainfall from May to October with a short interlude in mid-July to August.[6] During the winter months of November to March dry dust-laden harmattan winds blow inland causing many problems for residents.[6]
Liberia's watershed tends to move in a southwestern pattern towards the sea as new rains move down the forested plateau off the inland mountain range of Guinée Forestière, in Guinea. Cape Mount near the border with Sierra Leone receives the most precipitation in the nation.[6] The country's main northwestern boundary is traversed by the Mano River while its southeast limits are bounded by the Cavalla River.[6] Liberia's three largest rivers are St. Paul exiting near Monrovia, the river St. John at Buchanan and the Cestos River, all of which flow into the Atlantic. The Cavalla is the longest river in the nation at 515 kilometres (320 mi).[6]
Liberia's highest point is Mount Wuteve at 1,380 metres (4,500 ft) above sea level in the northwestern Liberia range of the West Africa Mountains and the Guinea Highlands.[6] However, Mount Nimba near Yekepa, is taller at 1,752 meters (5,748 ft) above sea level but is not wholly within Liberia as Nimba shares a border with Guinea and Côte d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast) and is their tallest mountain as well.[16]
Counties and districts
Liberia is divided into 15 counties, which are subdivided into districts, and further subdivided into clans. The counties are:
|
|
|
Economy
Historically, the Liberian economy depended heavily on iron ore and rubber exports, foreign direct investment, as well as the export of its other natural resources, such as timber.[6] Agricultural products include livestock (goats, pigs, cattle) and rice, the staple food.[6] Fish are raised on inland farms and caught along the coast.[6] Other foods are imported to support the population.[6] Electricity is provided by dams and oil-fired plants.[6]

Foreign trade was primarily conducted for the benefit of the Americo-Liberian elite, with trade between foreigners and indigenous Liberians severely restricted throughout most of its history by the 1864 Ports of Entry Act. Little foreign direct investment benefited the 95% majority population, who were often subjected to forced labor on foreign concessions. Liberian law often did not protect indigenous Liberians from the extraction of rents and arbitrary taxation, with the majority surviving on subsistence farming and low wage work on foreign concessions.
While official export figures for commodities declined during the 1990’s civil war as many investors fled, Liberia’s wartime economy featured the exploitation of the region’s diamond wealth, with the country acting as a major trader in Liberian, Sierra Leonian and Angolan blood diamonds, exporting over $300 million in diamonds annually. This led to a United Nations ban on Liberian diamond exports, which was lifted on April 27, 2007. Other commodity exports continued during the war, in part due to illicit agreements struck between Liberia’s warlords and foreign concessionaires. Looting and war profiteering destroyed nearly the entire infrastructure of the country, such that the Monrovian capital was without running water and electricity (except for fuel-powered generators) by the time the first elected post-war government began to institute development and reforms in 2006. Although some official exporting and legitimate business activity resumed once the hostilities ended (for instance, Liberia signed a new deal with steel giant Mittal for the export of iron ore in summer 2005), as of mid-2006 Liberia was dependent on foreign aid, and carried a debt overhang of $3.5 billion. Liberia currently[when?] has an approximate 85% unemployment rate, the second highest in the world, behind only Nauru.[citation needed]

The Liberia dollar currently trades against the US dollar at a ratio of 57:1. Liberia used the US dollar as its currency from 1943 until it reversed dollarization in 1982. Its external debt ($3.5 billion) is huge in comparison to its GDP (approx $2.5 billion/year); it annually imports approximately $4.839 billion in goods while it exports only about $910 million. Inflation is falling, but still significant (dropping from 15% in 2003 to 4.9% in the 3rd quarter of 2005); interest rates are high, with the average lending rate listed by the Central Bank of Liberia at 17.6% for 3rd quarter 2005 (although the average time deposit rate was only .4%, and CD rate only 4.4%, barely keeping pace with inflation). It continues to suffer with poor economic performance due to a fragile security situation, the devastation wrought by its long war, its lack of infrastructure, and necessary human capital to help the country recover from the scourges of conflict and corruption.[citation needed] Liberia has one of the world's largest national registries of ships, due to its status as a "flag of convenience".
Religion
The Christian community, accounts for 40 percent of the country's population. Also 40 percent of the population maintain Indigenous beliefs. And Muslims makes up the 20 percent of the population.[17]
Demographics
The population of over 3 million comprises 16 indigenous ethnic groups and various foreign minorities. Indigenous peoples comprise about 95% of the population, the largest of which are the Kpelle in central and western Liberia. Americo-Liberians, who are descendants of African-American settlers makeup 2.5% of the population and Congo people (descendants of repatriated Congo and Afro-Caribbean slaves who arrived in 1825) make up an estimated 2.5% of the population.[18][19] There also is a sizable number of Lebanese, Indians, and other West African nationals who make up a significant part of Liberia's business community. A few whites (estimated at 18,000 in 1999; probably fewer now) reside in the country.[19]
As of 2006, Liberia has the highest population growth rate in the world (4.50%). Similar to its neighbors, it has a large youth population, with half of the population being under the age of 18.
Culture

Liberia was traditionally noted for its hospitality, academic institutions, cultural skills, and arts/craft works— Liberia has a long, rich history in textile arts and quilting. The free and former US slaves who emigrated to Liberia brought with them their sewing and quilting skills. The 1843 Liberian census indicated a variety of occupations, including hatter, milliner, seamstress and tailor.[20] Liberia hosted National Fairs in 1857 and 1858 in which prizes were awarded for various needle arts. One of the most well-known Liberian quilters was Martha Ann Ricks,[21] who presented a quilt featuring the famed Liberian coffee tree to Queen Victoria in 1892.
In modern times, Liberian presidents would present quilts as official government gifts. The John F. Kennedy Library and Museum collection includes a cotton quilt by Mrs. Jemima Parker which has portraits of both Liberian president William Tubman and JFK. Zariah Wright-Titus founded the Arthington (Liberia) Women's Self-Help Quilting Club (1987). In the early 1990s, Kathleen Bishop documented examples of appliquéd Liberian quilts. When current Liberian President Ellen Johnson-Sirleaf moved into the Executive Mansion, she reportedly had a Liberian-made quilt installed in her presidential office.[22]
The tallest man-made structure of Africa, the mast of former Paynesville Omega transmitter is situated in Liberia.
Education

The University of Liberia is located in Monrovia. Opened in 1862, it is one of Africa's oldest institutes of higher learning. Civil war severely damaged the university in the 1990s, but the university has begun to rebuild following the restoration of peace.
Cuttington University was established by the Episcopal Church of the USA (ECUSA) in 1889; its campus is currently located in Suakoko, Bong County (120 miles north of Monrovia).
According to statistics published by UNESCO for 2004 65% of primary-school age and 24% of secondary-school age children were enrolled in school.[23] This is a significant increase on previous years, the statistics also show substantial numbers of older children going back to earlier school years.


No comments:
Post a Comment